Flerovium - 114Fl: properties of free atoms
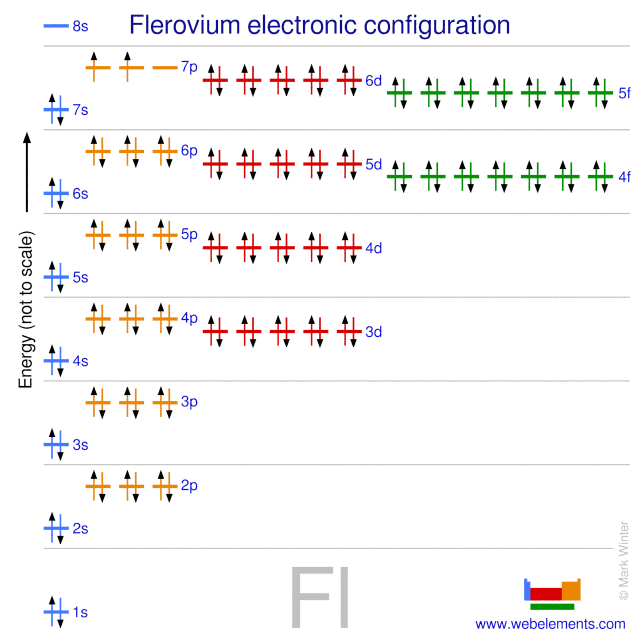
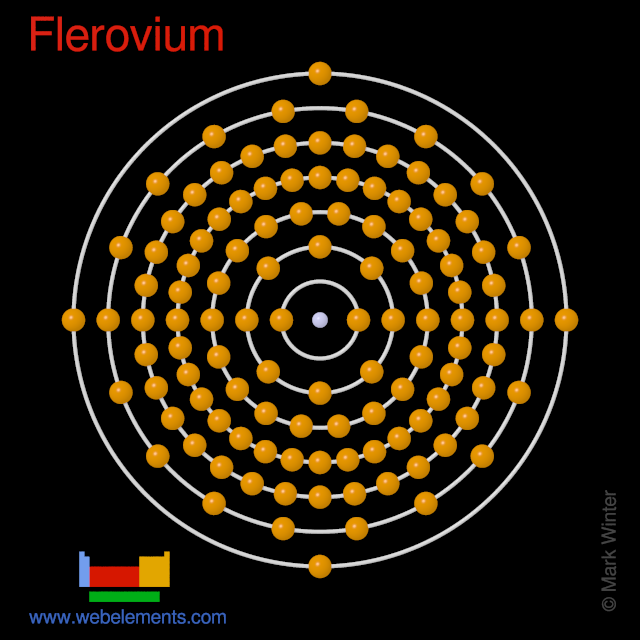
Flerovium atoms have 114 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.32.32.18.4.
The ground state electron configuration of ground state gaseous neutral flerovium is [Rn].5f14.6d10.7s2.7p2 (a guess based upon that of lead) and the term symbol is 3P0 (a guess based upon guessed electronic structure).
Atomic spectrum
A representation of the atomic spectrum of flerovium.
Ionisation Energies and electron affinity
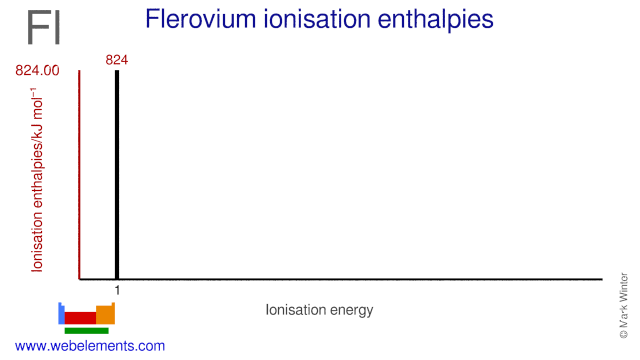
The electron affinity of flerovium is (no data) kJ mol‑1. The ionisation energies of flerovium are given below.
| Ionisation energy number | Enthalpy / kJ mol‑1 |
|---|---|
| 1st | 824 |
Effective Nuclear Charges
The following are "Clementi-Raimondi" effective nuclear charges, Zeff. Follow the hyperlinks for more details and for graphs in various formats.
| 1s | (no data) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2s | (no data) | 2p | (no data) | ||||
| 3s | (no data) | 3p | (no data) | 3d | (no data) | ||
| 4s | (no data) | 4p | (no data) | 4d | (no data) | 4f | (no data) |
| 5s | (no data) | 5p | (no data) | 5d | (no data) | ||
| 6s | (no data) | 6p | (no data) | ||||
| 7s | |||||||
References
These effective nuclear charges, Zeff, are adapted from the following references:
- E. Clementi and D.L.Raimondi, J. Chem. Phys. 1963, 38, 2686.
- E. Clementi, D.L.Raimondi, and W.P. Reinhardt, J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 47, 1300.
Electron binding energies
| Label | Orbital | eV [literature reference] |
|---|
Notes
I am grateful to Gwyn Williams (Jefferson Laboratory, Virginia, USA) who provided the electron binding energy data. The data are adapted from references 1-3. They are tabulated elsewhere on the WWW (reference 4) and in paper form (reference 5).
References
- J. A. Bearden and A. F. Burr, "Reevaluation of X-Ray Atomic Energy Levels," Rev. Mod. Phys., 1967, 39, 125.
- M. Cardona and L. Ley, Eds., Photoemission in Solids I: General Principles (Springer-Verlag, Berlin) with additional corrections, 1978.
- Gwyn Williams WWW table of values
- D.R. Lide, (Ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 81st edition, 2000.
- J. C. Fuggle and N. Mårtensson, "Core-Level Binding Energies in Metals," J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom., 1980, 21, 275.