Gold - 79Au: isotope data
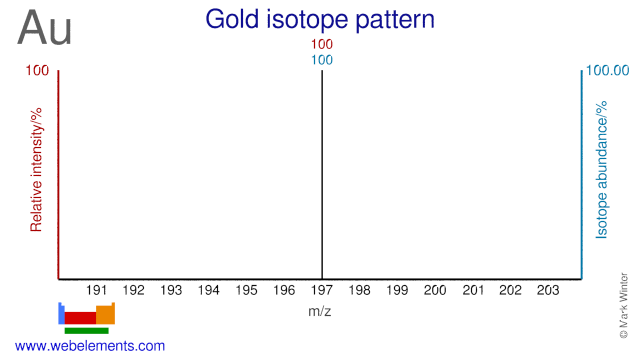
Gold is monoisotopic consisting completely of 197Au. However there are a number of radioisotopes, some of which are listed.
The gold isotope 198Au is used for treating cancer and other conditions. In the form of a gold colloid, 198Au has a diagnostic use for liver imaging and a therapeutic use in treatment of widespread abdominal carcinomatosis with ascites; carcinomatosis of pleura with effusion; lymphomas; interstitially in metastatic tumour. While there is a certain risk from the β-decay of 198Au the calculation is that the benefits outweight the risks.
Naturally occurring isotopes
| Isotope | Mass / Da | Natural abundance (atom %) | Nuclear spin (I) | Magnetic moment (μ/μN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 197Au | 196.966543 (4) | 100 | 3/2 | 0.148159 |
Radiosotope data
| Isotope | Mass / Da | Half-life | Mode of decay | Nuclear spin | Nuclear magnetic moment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 194Au | 193.96534 | 1.64 d | EC to 194Pt | 1 | 0.075 |
| 195Au | 194.965017 | 186.12 d | EC to 195Pt | 3/2 | 0.149 |
| 196Au | 196.966551 | 6.18 d | EC to 196Pt; β- to 196Hg | 2 | 0.591 |
| 198Au | 197.968225 | 2.694 d | β- to 198Hg | 2 | 0.5934 |
| 199Au | 198.968748 | 3.14 d | β- to 199Hg | 3/2 | 0.2715 |
References
- Naturally occurring isotope abundances: Commission on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Abundances report for the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry in Isotopic Compositions of the Elements 1989, Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1998, 70, 217. [Copyright 1998 IUPAC]
- For further information about radioisotopes see Jonghwa Chang's (Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute) Table of the Nuclides
- Masses, nuclear spins, and magnetic moments: I. Mills, T. Cvitas, K. Homann, N. Kallay, and K. Kuchitsu in Quantities, Units and Symbols in Physical Chemistry, Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, UK, 1988. [Copyright 1988 IUPAC]
NMR Properties of gold
Common reference compound: no defined reference.
| Isotope 1 | Isotope 2 | Isotope 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isotope | 197Au | ||
| Natural abundance /% | 100 | ||
| Spin (I) | 3/2 | ||
| Frequency relative to 1H = 100 (MHz) | 1.754000 | ||
| Receptivity, DP, relative to 1H = 1.00 | 0.0000277 | ||
| Receptivity, DC, relative to 13C = 1.00 | 0.158 | ||
| Magnetogyric ratio, γ (107 rad T‑1 s-1) | 0.473060 | ||
| Magnetic moment, μ (μN) | 0.191271 | ||
| Nuclear quadrupole moment, Q/millibarn | 547(16) | ||
| Line width factor, 1056 l (m4) | 0.29 |
References
- R.K. Harris in Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, D.M. Granty and R.K. Harris, (eds.), vol. 5, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, UK, 1996. I am grateful to Professor Robin Harris (University of Durham, UK) who provided much of the NMR data, which are copyright 1996 IUPAC, adapted from his contribution contained within this reference.
- J. Mason in Multinuclear NMR, Plenum Press, New York, USA, 1987. Where given, data for certain radioactive nuclei are from this reference.
- P. Pyykkö, Mol. Phys., 2008, 106, 1965-1974.
- P. Pyykkö, Mol. Phys., 2001, 99, 1617-1629.
- P. Pyykkö, Z. Naturforsch., 1992, 47a, 189. I am grateful to Professor Pekka Pyykkö (University of Helsinki, Finland) who provided the nuclear quadrupole moment data in this and the following two references.
- D.R. Lide, (ed.), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 1999-2000 : A Ready-Reference Book of Chemical and Physical Data (CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 79th edition, 1998.
- P. Pyykkö, personal communication, 1998, 204, 2008, 2010.