Strontium - 38Sr: the essentials
- Name: strontium
- Symbol: Sr
- Atomic number: 38
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 87.62 (1) g, r [see notes g r]
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery white
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 2
- Group name: Alkaline earth metal
- Period in periodic table: 5
- Block in periodic table: s
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.8.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-24-6
Strontium atoms have 38 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.8.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral strontium is [Kr].5s2 and the term symbol of strontium is 1S0.
Strontium: description
Strontium does not occur as the free element. Strontium is softer than calcium and decomposes water more vigorously. Freshly cut strontium has a silvery appearance, but rapidly turns a yellowish colour with the formation of the oxide. The finely divided metal ignites spontaneously in air. Volatile strontium salts impart an excellent crimson colour to flames, and these salts are used in pyrotechnics.

The picture above shows the colour arising from adding strontium sulphate salt (SrSO4) to a burning mixture of potassium chlorate and sucrose. Do not attempt this reaction unless are a professionally qualified chemist and you have carried out a legally satisfactory hazard assessment.
Strontium-90 (90Sr) has a half-life of 28 years. It is a product of nuclear fallout and presents a major health problem. Strontium titanate is an interesting optical material as it has an extremely high refractive index and an optical dispersion greater than that of diamond. It has been used as a gemstone, but it is very soft.

This sample is from The Elements Collection, an attractive and safely packaged collection of the 92 naturally occurring elements that is available for sale.
Strontium: physical properties
Density of solid: 2630 kg m-3
Molar volume: 33.94 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 35 W m‑1 K‑1
Strontium: heat properties
Melting point: 1050 [777 °C (1431 °F)] K
Boiling point: 1655 [1382 °C (2520 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Strontium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 200 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 185 (coordination number 2) ppm
van der Waals radius: 284 ppm
Strontium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 0.95 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 0.99 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 1.00 (sp orbital)
Strontium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 549.47 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1064.26 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 4137.63 kJ mol‑1
Strontium: abundances
Universe: 40 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 360000 ppb by weight
Human: 4600 ppb by weight
Strontium: crystal structure
Strontium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: 4600 ppb by weight
Strontium has no biological role.
Strontium: uses
Strontium: reactions
Reactions of strontium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Strontium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of strontium where known.
Strontium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of strontium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Strontium: history
Strontium was discovered by Adair Crawford in 1790 at Scotland. Origin of name: named after the village of "Strontian" in Scotland.Strontium: isotopes
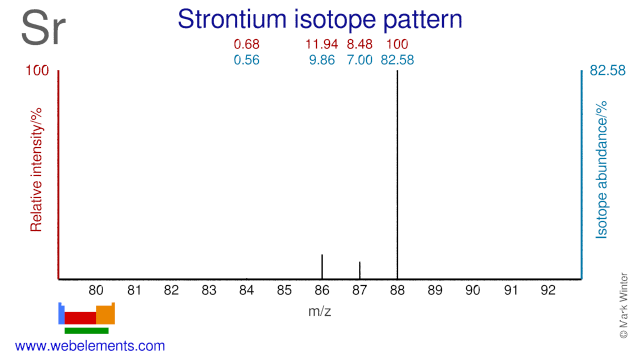
Strontium has four stable isotopes and two of them have medical applications. Sr-86 is used for the production of the PET isotope Y-86 which is used in dosimetry prior to Y-90 based radioimmunotherapy. Sr-88 is used for the production of Sr-89 which is the active agent in MetastronTM.
Strontium: isolation
Isolation: strontium metal is available commercially and there is no need to make it in the laboratory. Commercially it is made on small scale by the electrolysis of molten strontium chloride, SrCl2.
cathode: Sr2+(l) + 2e- → Sr
anode: Cl-(l) → 1/2Cl2 (g) + e-
Strontium metal can also be islated from the reduction of strontium oxide, SrO, with aluminium.
6SrO + 2Al → 3Sr + Sr3Al2O6