Barium - 56Ba: the essentials
- Name: barium
- Symbol: Ba
- Atomic number: 56
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 137.327 (7)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery white
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 2
- Group name: Alkaline earth metal
- Period in periodic table: 6
- Block in periodic table: s
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.18.8.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-39-3
Barium atoms have 56 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.18.8.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral barium is [Xe].6s2 and the term symbol of barium is 1S0.
Barium: description
Barium is a metallic element, soft, and when pure is silvery white like lead. The metal oxidises very easily and it reacts with water or alcohol. Barium is one of the alkaline-earth metals. Small amounts of barium compounds are used in paints and glasses.

Barium salts impart green colours to flames. The picture above shows the colour arising from adding barium chlorate (BaClO3) to a burning mixture (only to be carried out by a professionally qualified chemist).

Image adapted with permission from Prof James Marshall's (U. North Texas, USA) Walking Tour of the elements CD.
Barium: physical properties
Density of solid: 3510 kg m-3
Molar volume: 38.16 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 18 W m‑1 K‑1
Barium: heat properties
Melting point: 1000 [727 °C (1341 °F)] K
Boiling point: 2143 [1870 °C (3398 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Barium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 215 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 196 (coordination number 2) ppm
van der Waals radius: 303 ppm
Barium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 0.89 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 0.97 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 0.88 (sp orbital)
Barium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 502.85 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 965.22 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 3458.40 kJ mol‑1
Barium: abundances
Universe: 10 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 340000 ppb by weight
Human: 300 ppb by weight
Barium: crystal structure
Barium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: 300 ppb by weight
Barium has no biological role. The British Pharmaceutical Codex from 1907 indicates that barium chloride ["barii chloridum", BaCl2.2H2O] has a stimulant action on the heart and other muscles. It was said that it "raises blood pressure by constricting the vessels and tends to empty the intestines, bladder, and gall bladder". Its poisonous nature was also pointed out. Barium sulphide (BaS) was used as a depilatory agent (removes hair). Barium sulphate (BaSO4) is insoluble and used for body imaging (barium meal).
Barium: uses
Barium: reactions
Reactions of barium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Barium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of barium where known.
Barium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of barium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Barium: history
Barium was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1808 at England. Origin of name: from the Greek word "barys" meaning "heavy".Barium: isotopes
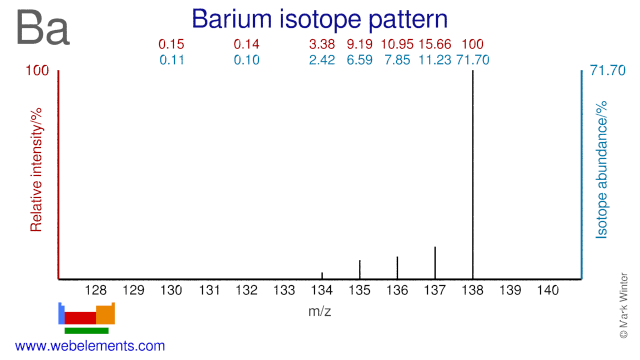
Barium isotopes are used in a wide variety of fields and applications. Ba-130 is used in the production of Ba-131/Cs-131 which is used in brachytherapy (seeds). Ba-132 can be used for the production of Ba-133 which is used as a gamma reference source. Ba-134 has been used to perform experiments in the field of nuclear physics. Ba-136 has been used to study photon scattering phenomena. Both Ba-136 and Ba-138 have been used in activation cross section experiments. Ba-135 has been used to validate the use of spinor symmetry while Ba-137 has been used in experiments regarding the theory of relativistic coupled clusters. Finally, Ba-138 has been used in studying so-called r- and s-processes in stars.
Barium: isolation
Isolation: barium metal is available commercially and there is normally no need to make it in the laboratory. Commercially, it is made on small scale by the electrolysis of molten barium chloride, BaCl2.
cathode: Ba2+(l) + 2e- → Ba
anode: Cl-(l) → 1/2Cl2 (g) + e-
Barium metal can also be islated from the reduction of barium oxide, BaO, with aluminium.
6BaO + 2Al→ 3Ba + Ba3Al2O6