Potassium - 19K: the essentials
- Name: potassium
- Symbol: K
- Atomic number: 19
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 39.0983 (1)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery white
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 1
- Group name: Alkali metal
- Period in periodic table: 4
- Block in periodic table: s
- Shell structure: 2.8.8.1
- CAS Registry: 7440-09-7
Potassium atoms have 19 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.8.1. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral potassium is [Ar].4s1 and the term symbol of potassium is 2S1/2.
Potassium: description
Potassium is a metal and is the seventh most abundant and makes up about 1.5 % by weight of the earth's crust. Potassium is an essential constituent for plant growth and it is found in most soils. It is also a vital element in the human diet.
Potassium is never found free in nature, but is obtained by electrolysis of the chloride or hydroxide, much in the same manner as prepared by Davy. It is one of the most reactive and electropositive of metals and, apart from lithium, it is the least dense known metal. It is soft and easily cut with a knife. It is silvery in appearance immediately after a fresh surface is exposed.
It oxidises very rapidly in air and must be stored under argon or under a suitable mineral oil. As do all the other metals of the alkali group, it decomposes in water with the evolution of hydrogen. It usually catches fire during the reaction with water. Potassium and its salts impart a lilac colour to flames.

The picture above shows the colour arising from a burning mixture of potassium chlorate (KClO3) and sucrose (only to be demonstrated by a professionally qualified chemist).
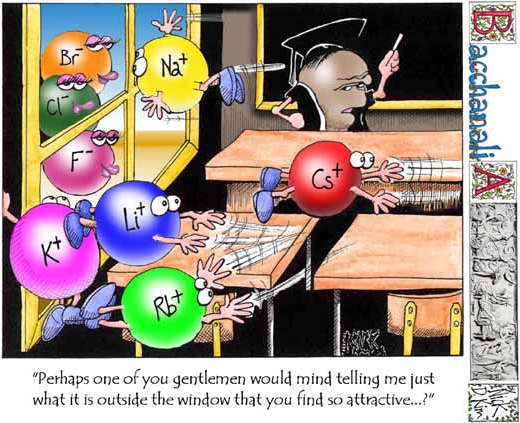
The chemistry of potassium is dominated by electron loss to form K+. Cartoon by Nick D Kim ([Science and Ink], used by permission).
Potassium: physical properties
Density of solid: 856 kg m-3
Molar volume: 45.94 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 100 W m‑1 K‑1
Potassium: heat properties
Melting point: 336.53 [63.38 °C (146.08 °F)] K
Boiling point: 1032 [759 °C (1398 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Potassium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 220 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 196 (coordination number 1) ppm
van der Waals radius: 273 ppm
Potassium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 0.82 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 0.91 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 0.73 (s orbital)
Potassium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 418.81 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 3051.35 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 4419.3 kJ mol‑1
Potassium: abundances
Universe: 3000 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 15000000 ppb by weight
Human: 2000000 ppb by weight
Potassium: crystal structure
Potassium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: 2000000 ppb by weight
Potassium salts are essential for both animals and plants. The potassium cation (K+) is the major cation in intracellular (inside cells) fluids (sodium is the main extracellular cation). It is essential for nerve and heart function. A normal diet containing reasonable amounts of vegetables contains all the potassium necessary.
Potassium: uses
Potassium: reactions
Reactions of potassium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Potassium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of potassium where known.
Potassium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of potassium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Potassium: history
Potassium was discovered by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1807 at England. Origin of name: from the English word "potash" (pot ashes) and the Arabic word "qali" meaning alkali (the origin of the symbol K comes from the Latin word "kalium").Potassium: isotopes
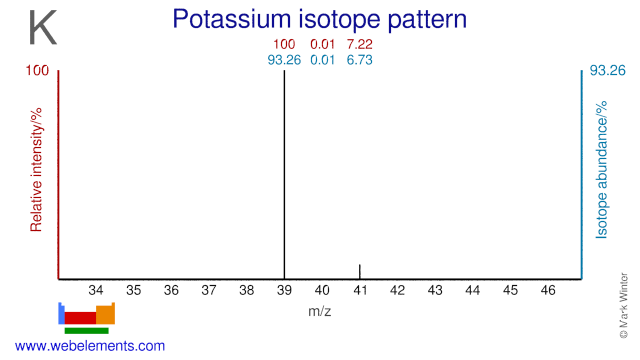
Although Potassium only has two stable isotopes (K-39 and K-41), the long-lived radioisotope K-40 is often also regarded as a stable isotope. Potassium isotopes, mainly K-40 and K-41, are used to study the impact of potassium on the growth of plants and of the human cardiovascular system.
Potassium: isolation
Isolation: potassium would not normally be made in the laboratory as it is so readily available commercially. All syntheses require an electrolytic step as it is so difficult to add an electron to the poorly electronegative potassium ion K+.
Potassium is not made by the same method as sodium as might have been expected. This is because the potassium metal, once formed by electrolysis of liquid potassium chloride (KCl), is too soluble in the molten salt.
cathode: K+(l) + e- → K (l)
anode: Cl-(l) → 1/2Cl2 (g) + e-
Instead, it is made by the reaction of metallic sodium with molten potassium chloride at 850°C.
Na + KCl ⇌ K + NaCl
This is an equilibrium reaction and under these conditions the potassium is highly volatile and removed from the system in a form relatively free from sodium impurities, allowing the reaction to proceed.
