Tungsten - 74W: the essentials
- Name: tungsten
- Symbol: W
- Atomic number: 74
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 183.84 (1)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: greyish white, lustrous
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 6
- Group name: (none)
- Period in periodic table: 6
- Block in periodic table: d
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.32.12.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-33-7
Tungsten atoms have 74 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.32.12.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral tungsten is [Xe].4f14.5d4.6s2 and the term symbol of tungsten is 5D0.
Tungsten: description
Pure tungsten is a steel-gray to tin-white metal. Tungsten has the highest melting point and lowest vapour pressure of all metals, and at temperatures over 1650°C has the highest tensile strength. The metal oxidises in air and must be protected at elevated temperatures. It has excellent corrosion resistance and is attacked only slightly by most mineral acids.

Small and large samples of tungsten wire like this, as well as foil, sheet, wire straight cut lengths, insulated wire, and mesh (and tungsten alloys in wire form), can be purchased from Advent Research Materials via their web catalogue.
Tungsten: physical properties
Density of solid: 19250 kg m-3
Molar volume: 9.47 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 174 W m‑1 K‑1
Tungsten: heat properties
Melting point: 3695 [3422 °C (6192 °F)] K
Boiling point: 5828 [5555 °C (10031 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Tungsten: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 135 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 137 (coordination number 6) ppm
van der Waals radius: 249 ppm
Tungsten: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 2.36 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.40 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: (no data)
Tungsten: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 758.76 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1580 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 2510 kJ mol‑1
Tungsten: abundances
Universe: 0.5 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 1100 ppb by weight
Human: (no data) ppb by weight
Tungsten: crystal structure
Tungsten: biological data
Human abundance by weight: (no data) ppb by weight
Tungsten has a limited biological role. A number of enzymes (oxidoreductases) employ tungsten in a way related to molybdenum, (using tungsten.pterin complex). The structure of a tungstoenzyme aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase is known (Protein Data Bank code 1AOR).
Tungsten: uses
Tungsten: reactions
Reactions of tungsten as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Tungsten: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of tungsten where known.
Tungsten: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of tungsten halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Tungsten: history
Tungsten was discovered by Fausto and Juan Jose de Elhuyar in 1783 at Spain. Origin of name: from the Swedish words "tung sten" meaning "heavy stone" (the origin of the symbol W is "wolfram ", named after the tungsten mineral wolframite).Tungsten: isotopes
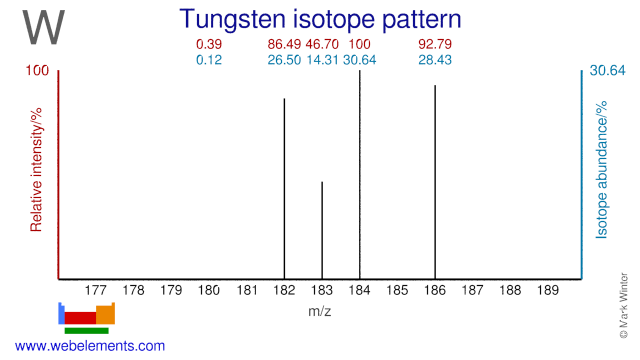
Tungsten isotopes are used in several applications. W-180 is used for the production of the therapeutic radioisotope W-181. W-186 is used for the production of W-188 which is used in so-called Tungsten-Rhenium generators. The W-188 daughter Re-188 is (milked( from there generators and used as a therapeutic radioisotope. W-184 has been used to study the elastic and inelastic scattering of heavy ions.
Tungsten: isolation
Isolation: coming soon!