Rhenium - 75Re: the essentials
- Name: rhenium
- Symbol: Re
- Atomic number: 75
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 186.207 (1)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: greyish white
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 7
- Group name: (none)
- Period in periodic table: 6
- Block in periodic table: d
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.32.13.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-15-5
Rhenium atoms have 75 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.32.13.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral rhenium is [Xe].4f14.5d5.6s2 and the term symbol of rhenium is 6S5/2.
Rhenium: description
Rhenium is silvery white with a metallic lustre; its density is exceeded only by that of platinum, iridium, and osmium, and its melting point is exceeded only by that of tungsten and carbon. It has other useful properties. It is expensive but useful as a trace alloying agent.

Rhenium wire.
Rhenium: physical properties
Density of solid: 21020 kg m-3
Molar volume: 8.86 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 48 W m‑1 K‑1
Rhenium: heat properties
Melting point: 3459 [3186 °C (5767 °F)] K
Boiling point: 5869 [5596 °C (10105 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Rhenium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 135 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 131 (coordination number 5) ppm
van der Waals radius: 248 ppm
Rhenium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 1.9 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.46 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: (no data)
Rhenium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 755.82 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1600 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 2610 kJ mol‑1
Rhenium: abundances
Universe: 0.2 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 2.6 ppb by weight
Human: (no data) ppb by weight
Rhenium: crystal structure
Rhenium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: (no data) ppb by weight
Rhenium has no biological role.
Rhenium: uses
Rhenium: reactions
Reactions of rhenium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Rhenium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of rhenium where known.
Rhenium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of rhenium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Rhenium: history
Rhenium was discovered by Walter Noddack, Ida Tacke, Otto Berg in 1925 at Germany. Origin of name: from the Greek word "Rhenus" meaning river "Rhine".Rhenium: isotopes
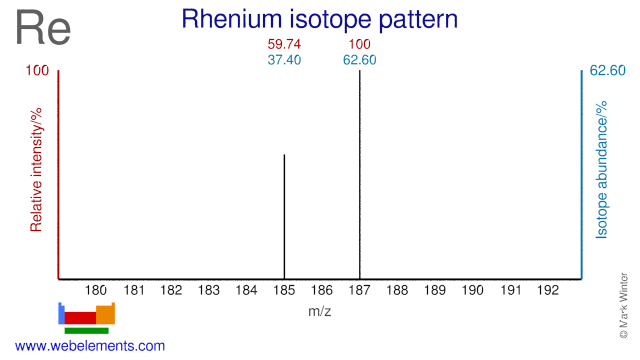
Both Rhenium isotopes are used for medical purposes. Re-185 is used for the production of Re-186 which is used for bone pain palliation. Re-187 can be used for the production of Re-188 which is used for cancer therapy and restenosis, though most Re-188 is produced via W-186.
Rhenium: isolation
Isolation: coming soon!