Atomic radii (density cutoff)
Many references give table of atomic radii. Sometimes in text books and other sources, the rather vague term "atomic radius" is not defined and in such cases it is therefore not clear what the values actually mean. The values given here for atomic radius are calculated values using methods outlined in reference 1.
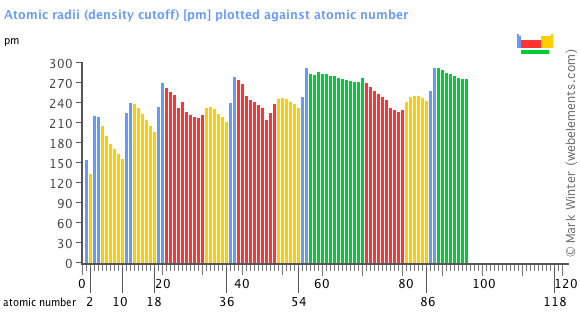
The definition of this form of atomic radius is based upon the electron density of isolated atoms in the atomic ground state and is the average distance from the nucleus where the electron density falls to 0.001 electrons per bohr3. These radii are derived using relativistic all-electron density functional theory calculations. They offer a systematic quantitative measure of the sizes of non-interacting atoms (commonly invoked in the rationalisation of chemical bonding, structure, and other properties. These atomic radii correlate well with van der Waals radii derived from crystal structures.
Units
pm
Notes
None
Select from the following links to see visual periodicity representations for atomic radii, covalent radii, and van der Waals radii. Ionic radii are also available.
- Atomic radii
- Atomic radii (empirical)
- Atomic radii (absolute)
- Atomic radii (density cutoff)
- Covalent radii
- Covalent radii revisited (2008 values)
- Covalent radii (molecular single bond)
- Covalent radii (molecular double bond)
- Covalent radii (molecular triple bond)
- Van der Waals radius
Literature sources
- M. Rahm, R. Hoffmann, and N.W. Ashcroft, Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 14625-14632.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1
|
2
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
3
|
4
|
5
|
6
|
7
|
8
|
9
|
10
|
|||||||||||
|
11
|
12
|
13
|
14
|
15
|
16
|
17
|
18
|
|||||||||||
|
19
|
20
|
21
|
22
|
23
|
24
|
25
|
26
|
27
|
28
|
29
|
30
|
31
|
32
|
33
|
34
|
35
|
36
|
|
|
37
|
38
|
39
|
40
|
41
|
42
|
43
|
44
|
45
|
46
|
47
|
48
|
49
|
50
|
51
|
52
|
53
|
54
|
|
|
55
|
56
|
* |
71
|
72
|
73
|
74
|
75
|
76
|
77
|
78
|
79
|
80
|
81
|
82
|
83
|
84
|
85
|
86
|
|
87
|
88
|
** |
103
|
104
|
105
|
106
|
107
|
108
|
109
|
110
|
111
|
112
|
113
|
114
|
115
|
116
|
117
|
118
|
| *Lanthanoids | * |
57
|
58
|
59
|
60
|
61
|
62
|
63
|
64
|
65
|
66
|
67
|
68
|
69
|
70
|
|||
| **Actinoids | ** |
89
|
90
|
91
|
92
|
93
|
94
|
95
|
96
|
97
|
98
|
99
|
100
|
101
|
102
|
|||