Manganese - 25Mn: the essentials
- Name: manganese
- Symbol: Mn
- Atomic number: 25
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 54.938044 (3)
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery metallic
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 7
- Group name: (none)
- Period in periodic table: 4
- Block in periodic table: d
- Shell structure: 2.8.13.2
- CAS Registry: 7439-96-5
Manganese atoms have 25 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.13.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral manganese is [Ar].3d5.4s2 and the term symbol of manganese is 6S5/2.
Manganese: description
Manganese metal is gray-white, resembling iron, but is harder and very brittle. The metal is reactive chemically, and decomposes cold water slowly. Manganese is widely distributed throughout the animal kingdom. It is an important trace element and may be essential for utilisation of vitamin B. Manganese is present in quantity the floor of oceans. It is an important component of steel.

Image adapted with permission from Prof James Marshall's (U. North Texas, USA) Walking Tour of the elements CD.
Cartoon by Nick D Kim ([Science and Ink], used by permission).
Manganese: physical properties
Density of solid: 7470 kg m-3
Molar volume: 7.35 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 7.8 W m‑1 K‑1
Manganese: heat properties
Melting point: 1519 [1246 °C (2275 °F)] K
Boiling point: 2334 [2061 °C (3742 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Manganese: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 140 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 119 (coordination number 5) ppm
van der Waals radius: 245 ppm
Manganese: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 1.55 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.60 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: (no data)
Manganese: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 717.28 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1509.03 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 3248.5 kJ mol‑1
Manganese: abundances
Universe: 8000 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 1100000 ppb by weight
Human: 200 ppb by weight
Manganese: crystal structure
Manganese: biological data
Human abundance by weight: 200 ppb by weight
Manganese compounds are essential to life. They are essential for the action of some enzymes. Soil deficiencies lead to infertility in mammals and to bone malformation in growing chicks.
Manganese: uses
Manganese: reactions
Reactions of manganese as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Manganese: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of manganese where known.
Manganese: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of manganese halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Manganese: history
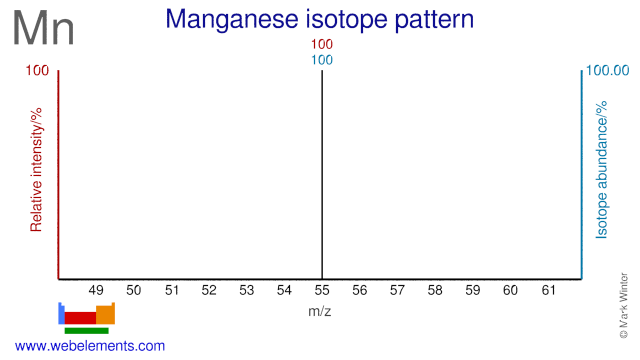
Manganese was discovered by Johann Gahn in 1774 at Sweden. Origin of name: from the Latin word "magnes" meaning "magnet", or "magnesia nigri" meaning "black magnesia" (MnO2).Manganese: isotopes
Manganese: isolation
Isolation: it is not normally necessary to make manganese in the laboratory as it is available commercially. Nearly all manganese produced commercially is used in the steel industry as ferromanganese. This made by the reduction of iron oxide, Fe2O3, and managanese dioxide, MnO2, in appropriate proportions with carbon (as coke) in a blast furnace. Pure manganese is available through the electrolysis of manganese sulphate, MnSO4,