Cadmium - 48Cd: the essentials
- Name: cadmium
- Symbol: Cd
- Atomic number: 48
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 112.414 (4) g [see note g]
- Standard state: solid at 298 K
- Appearance: silvery grey metallic
- Classification: Metallic
- Group in periodic table: 12
- Group name: (none)
- Period in periodic table: 5
- Block in periodic table: d
- Shell structure: 2.8.18.18.2
- CAS Registry: 7440-43-9
Cadmium atoms have 48 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.18.18.2. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral cadmium is [Kr].4d10.5s2 and the term symbol of cadmium is 1S0.
Cadmium: description
Cadmium is a soft, bluish-white metal and is easily cut with a knife. It is similar in many respects to zinc. Interestingly, aa characteristic cadmium "scream" is heard on bending a cadmium bar (such as that illustrated above). Cadmium and its compounds are highly toxic. Silver solder, which contains cadmium, should be handled with care.

Cartoon by Nick D Kim ([Science and Ink], used by permission).
Cadmium: physical properties
Density of solid: 8650 kg m-3
Molar volume: 13.00 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 97 W m‑1 K‑1
Cadmium: heat properties
Melting point: 594.22 [321.07 °C (609.93 °F)] K
Boiling point: 1040 [767 °C (1413 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Cadmium: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): 155 pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 136 (coordination number 1) ppm
van der Waals radius: 249 ppm
Cadmium: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: 1.69 (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 1.46 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 1.53 (sp orbital)
Cadmium: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 867.77 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 1631.40 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 3615.1 kJ mol‑1
Cadmium: abundances
Universe: 2 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 150 ppb by weight
Human: 700 ppb by weight
Cadmium: crystal structure

Cadmium: biological data
Human abundance by weight: 700 ppb by weight
Cadmium might be a necessary element in very, very, small quantities in rats.
Inhalation of cadmium dust causes problems for the respiratory tract and for the kidneys. Death may follow. Ingestion of any significant amount of cadmium causes immediate poisoning and damage to the liver and the kidneys.
Cadmium: uses
Cadmium: reactions
Reactions of cadmium as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Cadmium: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of cadmium where known.
Cadmium: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of cadmium halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Cadmium: history
Cadmium was discovered by Friedrich Strohmeyer in 1817 at Germany. Origin of name: somewhat confusingly, from the Latin word "cadmia" meaning "calamine" (zinc carbonate, ZnCO3) and from the Greek word "kadmeia" with the same meaning..Cadmium: isotopes
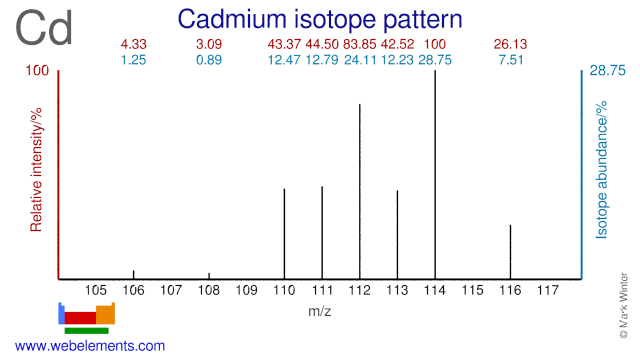
The nine stable Cadmium isotopes are used for many different purposes. Cd-110 is used for the production of the radioisotope In-110, while Cd-112 is used in the production of the widely used diagnostic radioisotope In-111. Cd-108 is used in the production of Cd-109 which is a calibration source for 88 keV gamma radiation. The even numbered Cd isotopes (mainly Cd-110, Cd-112, Cd-114 and Cd-116) are used to improve the power output and coherence length of HeCd lasers.
Cadmium: isolation
Isolation: it is rare that preparation of cadmium in the laboratory should be required bacause of environmental concerns about cadmium. The isolation of cadmium is associated with zinc recovery as cadmium is an impurity in zinc ores. Most zinc production is based upon sulphide ores. These are roasted in industrial plants to form zinc oxide, ZnO. This may be reduced with carbon to form zinc metal, but in practice ingenious technology is required to ensure that the resulting zinc does not contain oxide impurities.
ZnO + C → Zn + CO
ZnO + CO → Zn + CO2
CO2 + C → 2CO
After this process, zinc may be refined by distillation under vacuum and this process also allows the separation of any cadmium present in the crude zinc.
The other type of extraction of zinc is electrolytic. Dissolution of crude zinc oxide, ZnO, in sulphuric acid gives zinc sulphate, ZnSO4 in solution. Before electrolysis to produce zinc, the cadmium impurity and is removed as a precipitate by the addition of zinc dust as cadmium sulphate.