Argon - 18Ar: the essentials
- Name: argon
- Symbol: Ar
- Atomic number: 18
- Relative atomic mass (Ar): 39.948 (1) g, r [see notes g r]
- Standard state: gas at 298 K
- Appearance: colourless
- Classification: Non-metallic
- Group in periodic table: 18
- Group name: Noble gas
- Period in periodic table: 3
- Block in periodic table: p
- Shell structure: 2.8.8
- CAS Registry: 7440-37-1
Argon atoms have 18 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8.8. The ground state electronic configuration of neutral argon is [Ne].3s2.3p6 and the term symbol of argon is 1S0.
Argon: description
Argon is a colourless and odourless gas present to a very small extent in the atmosphere. Argon is very inert (indeed it is referred to as one of the noble gases) and is not known to form true chemical compounds. It makes a good atmosphere for working with air-sensitive materials since it is heavier than air and less reactive than N2. Today, the chemical symbol for argon is Ar but until 1957 its sybol was simply A.

Image adapted with permission from Prof James Marshall's (U. North Texas, USA) Walking Tour of the elements CD.
Argon: physical properties
Density of solid: 1616 kg m-3
Molar volume: 22.56 cm3
Thermal conductivity: 0.01772 W m‑1 K‑1
Argon: heat properties
Melting point: 83.8 [‑189.3 °C (‑308.7 °F)] K
Boiling point: 87.3 [‑185.8 °C (‑302.4 °F)] K
Enthalpy of fusion: 20.5 kJ mol-1
Argon: atom sizes
Atomic radius (empirical): (no data) pm
Molecular single bond covalent radius: 96 (coordination number 1,2) ppm
van der Waals radius: 183 ppm
Argon: electronegativities
Pauling electronegativity: (no data) (Pauling units)
Allred Rochow electronegativity: 3.20 (Pauling units)
Mulliken-Jaffe electronegativity: 3.19 (12.5% s orbital)
Argon: orbital properties
First ionisation energy: 1520.57 kJ mol‑1
Second ionisation energy: 2665.86 kJ mol‑1
Third ionisation energy: 3930 kJ mol‑1
Argon: abundances
Universe: 200000 ppb by weight
Crustal rocks: 1500 ppb by weight
Human: (no data) ppb by weight
Argon: crystal structure
Argon: biological data
Human abundance by weight: (no data) ppb by weight
Argon has no biological role.
Argon: uses
Argon: reactions
Reactions of argon as the element with air, water, halogens, acids, and bases where known.
Argon: binary compounds
Binary compounds with halogens (known as halides), oxygen (known as oxides), hydrogen (known as hydrides), and other compounds of argon where known.
Argon: compound properties
Bond strengths; lattice energies of argon halides, hydrides, oxides (where known); and reduction potentials where known.
Argon: history
Argon was discovered by Sir William Ramsay, Lord Rayleigh in 1894 at UCL, London, England. Origin of name: from the Greek word "argos" meaning "inactive".Argon: isotopes
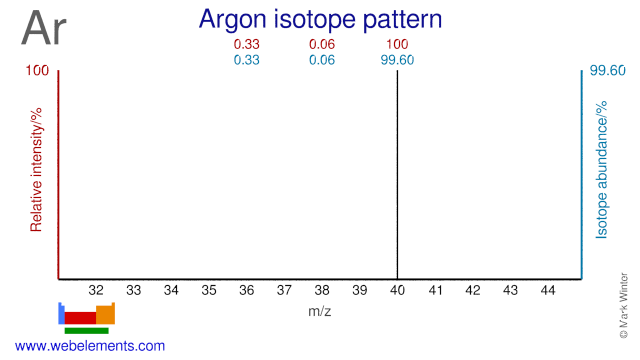
Argon isotopes are used as precursors in the production of radioisotopes. Ar-40 and Ar-38 are used in the production of radioactive K-38 which can be used as a blood flow tracer. Ar-40 is used in the production of radioactive Ar-41 which is used to trace gas flows.
Argon: isolation
Isolation: argon is present to a small extent in the atmosphere and is obtained as a byproduct from the liquefaction and separation of air. This would not normally be carried out in the laboratory and argon is available commercially in cylinders at high pressure.